Get Started
How to leverage advanced geospatial search and query functions
Overview
The Datasets API is a versatile and powerful tool designed to manage, query, and interact with geospatial data. A dataset serves as an editable collection of features, which can include points, lines, or polygons. The API is particularly well-suited for applications where location or spatial analysis are crucial, providing high accuracy analysis and flexibility in managing geospatial data.
Key concepts
Datasets: Collections of features, which are fundamental units for storing and managing geospatial data via the API.
Features: Individual elements within datasets, such as points, lines, or polygons, each defined by their geometry
(location and shape) and properties (descriptive attributes).
Core capabilities
- High Accuracy Storage: The Datasets API is built to store geospatial features with precision, making it ideal for business processes that depend on accurate location data.
- Versatile Geospatial Features: Supports basic geospatial shapes, including Points, LineStrings, and Polygons, though it does not support complex GeometryCollections or null geometries.
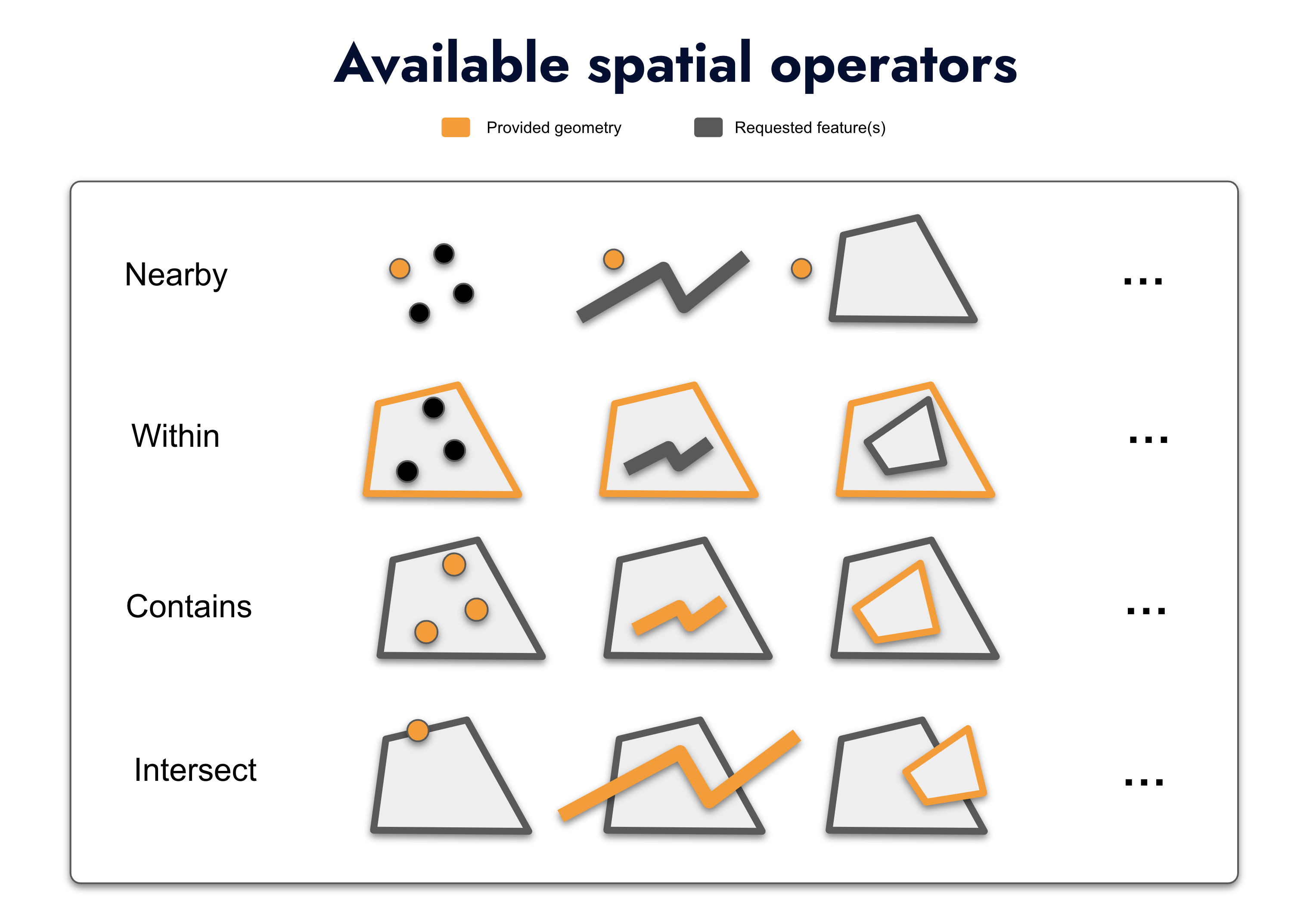
- Full set of Spatial Operators: Proposes most common spatial analysis (contains, intersect, within, nearby) that are key for business processes involving location.
Advanced Search and Query capabilities
The Datasets API stands out with its robust search functionality, enabling powerful and precise queries on stored geospatial data. The API offers several key endpoints tailored to specific types of geospatial searches:
/nearby: Allows you to find features within a specified distance from a given point. It’s perfect for applications
where proximity is important, such as finding the nearest store locations, service centres, or other points of interest
relative to a user’s location.
/contains: Search for features that completely contain a specific point or geometry. This is particularly useful
in scenarios such as identifying the region or zone in which a particular location falls, or determining whether a point
is inside a defined boundary, like a delivery area.
/intersect: Find features that intersect with a given geometry. This capability is essential for more complex
spatial analyses, such as identifying overlapping territories, intersecting routes, or shared boundaries between
different geographic areas.
/within: Search for features that are entirely within a specified bounding geometry. This is useful for filtering
features to those that fall inside a particular area, such as finding all points of interest within a city’s limits or
all assets within a designated operational zone.
Scalability and Flexibility
The Datasets API is designed to scale with your application’s needs, from handling simple location-based searches to supporting complex geospatial queries across large datasets. Its flexible querying options make it adaptable to a wide range of use cases, ensuring that you can retrieve and analyse spatial data in the most efficient way possible.
Example
Here is a sample of Datasets API calls using our Map-JS library. It allows you to test querying different dataset according to the chosen operator and the geomertry drawn on the map. API results are used to display a basic left panel with data associated, in addition to bounding boxes on the map of the retrieved features.
Supported files
Datasets can be loaded to Woosmap via zipped Shapefiles.
Default maximum supported file size is 20Mo. You can contact us if you need to load larger files.
Activating the product
Please contact us to make this product available for your Organisation.
Public and Private keys
Upon signing up to Woosmap, you will have access to the API key management interface in each project.
| key | Description |
|---|---|
| private_key1 | A private key is used for server API calls (POST, PUT and DELETE) where modification of the data occurs. |
| key | A public key is used client side to fetch or request your dataset. |
API Reference
Find all the details on supported methods, available endpoints, response formats and handled errors in our API reference doc here.
-
The private key holds destructive power hence it should remain private, the public key can be made public since it’s used client side. ↩